Tert-butyl
Group Substitution in the Ring-B of Murrayanine-Chalcone leads to
Higher Expression of Edema Reduction
Debarshi
Kar Mahapatra 1*,
Ruchi S. Shivhare 2,
Shilpa S. Borkar 3
1
Department of
Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Dadasaheb Balpande College of Pharmacy,
Nagpur, Maharashtra, India
2
Departments of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Kamla Nehru College of
Pharmacy, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India
3
Departments of Pharmacology, Kamla Nehru College of Pharmacy, Nagpur,
Maharashtra, India
Correspondence:
Email- dkmbsp@gmail.com
Abstract
Inspiring
from the fact that the free-radicals are the main culprit in the
precipitation of inflammation, cancer, and several other diseases, a
hybrid molecule comprising of murrayanine (carbazole moiety),
chalcone, and tert-butyl group was fabricated by our group, and it
showed enhanced anti-oxidant activity due to the synergistic effect
of the three individual components. These three components, in
individuality, have a strikingly high anti-oxidant activity.
Similarly, motivating from the above reports and data obtained from
the previously performed anti-oxidant studies, at present the
developed chalcone molecule was screened for its anti-inflammatory
potentials for treating chronic conditions such as rheumatoid
arthritis which involves the participation of free-radicals and the
management requires complete free-radical scavenging. The in vivo
anti-inflammatory screening was performed by employing the
carrageenan-induced paw edema method. The compound through the
tert-butyl group exhibited potential anti-inflammatory activity with
64.69% inhibition of edema after 3 hrs, probably by the inhibition of
the mediators like cyclooxygenase-1/2 and lipoxygenase. As compared
to the previously synthesized murrayanine-chalcones, either
unsubstituted or substituted by electron-withdrawing /
electron-donating groups, the chalcone exhibited much better
activity. The study opened new avenues of research by encouraging
medicinal chemists in understanding the strategies and approach
toward fabricating more potent analogs.
Keywords:
Murrayanine, Chalcone, tert-butyl, Anti-inflammatory, Anti-oxidant,
Edema
INTRODUCTION
Rheumatoid
arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition caused by the
auto-immune response in the human body [1]. It is often characterized
by inflamed joints and massive infiltration of macrophages and
T-cells which produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive
nitrogen species (RNS) and aggravates the pathological conditions.
The enhanced levels of isoprostanes and prostaglandins in the serum
are the chief markers of oxidative stress [2]. Millions of patients
of age more than 50 of both the sexes are affected by this disease
across the globe (in both developing and developed nations) and is
expected to rise nearly twice by the end of the year 2050 [3].
In
general, the human body produces more than 20,000 free-radicals every
day which has a delirious effect on molecular constitution [4].
Additionally, the long duration exposure to the environmental
contaminants such as industrial effluents, contaminated low-grade
food additives, cigarette smoking and exceptional lifestyle
practices, and excessive alcohol consumption doubles up these
inflammatory conditions [5]. Thereby, it can be predicted that person
with a chronic inflammatory state has two-fold oxidative stress than
a normal disease-free individual, which sturdily supported the direct
relationship between free-radical and chronic inflammatory state [6].
At present, there are a number of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
agents (NSAIDs) which are generally prescribed by medical
practitioners for the management of these conditions [7].
Inspiring
from the fact that the free-radicals are the main culprit in
precipitating the inflammation, cancer, and several other diseases
[8], a hybrid molecule comprising of murrayanine (carbazole moiety),
chalcone, and tert-butyl group was fabricated by our group, and it
showed enhanced anti-oxidant activity due to the synergistic effect
of the three individual components. These three components, in
individuality, have a strikingly high anti-oxidant activity [9].
Murrayanine
is a carbazole-based alkaloid obtained from Murraya koenigii (Family:
Rutaceae) having a noteworthy anti-oxidant effect [10]. The
semi-synthetic derivatives have extraordinarily higher anti-oxidant
and edema reducing perspectives [11-13]. Individually, the carbazole
synthetic molecules have both inflammation controlling and
free-radical scavenging potentials [14]. Chalcones are the
low-molecular-weight natural ligands having tremendous anti-oxidant
and anti-inflammatory effect [15-16]. The artificially developed
commercial anti-oxidants such as tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ),
2-tert-butyl-4-methoxyphenol (BHA), 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenol (TBP),
and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT), have tert-butyl group
which scavenges the free-radicals and have been recently screened for
edema reducing potentials where an outstanding anti-inflammatory
activity have been perceived [17].
Similarly,
motivating from the above reports and data obtained from the
previously performed anti-oxidant studies, at present the developed
chalcone molecule (Figure 1) was screened for its anti-inflammatory
potentials for treating chronic conditions such as rheumatoid
arthritis which involves the participation of free-radicals and the
management requires complete free-radical scavenging. The in vivo
anti-inflammatory screening was performed in Swiss albino rats by
employing the carrageenan-induced paw edema method.
MATERIALS
AND METHODS
Chemicals
The
analytical grade chemicals, solvents, and reagents for
anti-inflammatory screening were procured from HiMedia Ltd., India.
The
(E)-3-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-1-(1-methoxy-9H-carbazol-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one
was one of our previous reports and taken from our compound library
[9].
Animals
The
anti-inflammatory screening was performed on Swiss albino rats of age
5-6 weeks and weights in the range of 190-260 g were employed after
obtaining ethical permission from DEC and CPCSEA. The experimental
animals were kept in polypropylene cages under the hygienic
conditions of 25–26ºC / 50–55% RH / 12 dark 12 light cycle in
the registered departmental animal house.
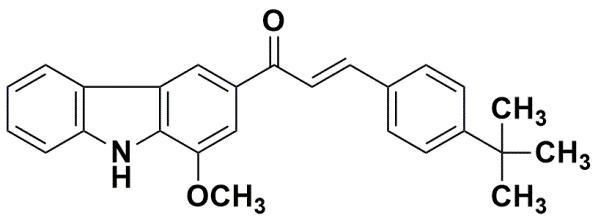
Figure
1. Tert-butyl group containing murrayanine-chalcone.
Table
1. In
vivo anti-inflammatory
potential of
(E)-3-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-1-(1-methoxy-9H-carbazol-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one.
|
Compound
|
Percentage
(%) inhibition of edema
|
|
|
1
hr
|
2
hr
|
3
hr
|
|
Chalcone
|
39.88**
± 1.97
|
50.72*
± 1.46
|
64.69*
± 1.55
|
|
Indomethacin
|
45.21**
± 1.33
|
58.33*
± 1.62
|
77.16**
± 1.41
|
n
= 6; ED50
of 200 mg/kg b.w. in male adult albino mice; **P < 0.01; *P<
0.05
Acute
toxicity studies
An
acute toxicity study was performed to estimate the highest safe dose
which will exert the maximum therapeutic effect without showing any
distinct sign and symptoms of toxicity along with the mortality. The
protocol involved injecting the chalcone compound in escalating dose
range of 25 mg/kg to 500 mg/kg in adult male albino rats. The lethal
dose (LD50) was established based on calculating the dose at which
50% animal died [18].
Anti-inflammatory
screening
The
in vivo anti-inflammatory screening of chalcone was performed
according to the standard carrageenan-induced paw edema method. The
albino rats were fasted overnight to reduce the inconsistencies while
recording the edema. 5 mL distilled water was administered orally
before commencing the study. An hour before the induction of
inflammation
by injecting 1% carrageenan solution at the subplanter region of the
right hind paw through subcutaneous route, the chalcone molecule (200
mg/kg b.w.) was suspended in the saline solution and administered
orally. The control group was administered saline solution (0.9%).
The thickness of each rat paw was measured using the mercury digital
micrometer for the duration of 3 hrs at an interval of 1 hr. The
disparity in the width of non-injected paws and injected paws were
determined to calculate appropriately the edema reducing potential of
the chalcone compound. The data were expressed as mean ± standard
error [19].
Statistical
treatment
The
procured anti-inflammatory data were treated by one-way ANOVA method
followed by treating with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. A P
value of <0.01 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
AND DISCUSSION
Anti-inflammatory
activity
A
significant high inflammatory activity has been noticed for the
chalcone compound and also demonstrated an analogous activity with
that of indomethacin. The compound through the tert-butyl group
exhibited potential anti-inflammatory activity with 64.69% inhibition
of edema after 3 hrs (Table-1), probably by the inhibition of the
mediators like cyclooxygenase-1/2 (COX-1/2) and lipoxygen-ase (LOX).
As compared to the previously synthesized murrayanine-chalcones,
either unsubstituted or substituted by electron-withdrawing /
electron-donating groups, the tert-butyl group containing chalcone
exhibited much better activity [12-13]. The reason may be better
free-radical (hydroxyl, superoxide anion, reactive nitrogen species,
etc.) scavenging by the synergistic activity of the three components
(murrayanine, chalcone, and tert-butyl), which are generated by the
inflammatory mediators.
CONCLUSION
This
motivating research highlighted that hybridization of three
components; murrayanine (carbazole), chalcone, and tert-butyl
exhibited a strikingly high edema reducing activity (64.69%
inhibition in 3 hrs) by scavenging the free-radical (hydroxyl,
superoxide anion, reactive nitrogen species, etc.) produced by the
mediators like COX-1/2 and lipoxygenase LOX, through synergistic
activity. The study also revealed that this murrayanine-chalcone
molecule expressed higher pharmacological activity than the
previously developed electron-withdrawing / electron-donating groups
containing murrayanine-chalcone compounds. The study opened new
avenues of research by encouraging medicinal chemists in
understanding the strategies and approach toward fabricating more
potent analogs.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Authors
are highly thankful to Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune,
Maharashtra, India for providing research grants (Grant No.
13PHM000126).
CONFLICT
OF INTEREST
No
conflict of interest declared.
REFERENCES
-
Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK. Drug
Design. New Delhi: Tara Publications Private Limited, 2016.
-
Mahapatra DK, Dadure KM,
Shivhare RS. Edema Reducing Potentials of Some Emerging Schiff’s
bases of Murrayanine. MOJ Bioorg Org Chem 2018; 2(4): 172-175.
-
Chhajed SS, Bastikar V, Bastikar
AV, Mahapatra DK. Computer Aided Drug Design. Pune: Everest
Publishing House, 2019.
-
Kamble MA, Mahapatra DK,
Dhabarde DM, Ingole AR. Pharmacognostic and pharmacological studies
of Bombax ceiba thorn extract. J Pharm Pharmacog Res 2017; 5(1):
40-54.
-
Mahapatra DK, Shivhare RS, Ugale
VG. Anti-inflammatory potentials of some novel Murrayanine
containing 1,3,4-Oxadiazole derivatives. Asian J Pharm Technol 2018;
8(1): 47-51.
-
Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK,
Editors. Medicinal Chemistry with Pharmaceutical Product
Development. New Jersey: Apple Academic Press, 2019.
-
Chhajed SS, Upasani CD, Wadher
SJ, Mahapatra DK. Medicinal Chemistry. Nashik: Career Publications
Private Limited, 2017.
-
Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK.
Handbook of Research on Medicinal Chemistry: Innovations and
Methodologies. New Jersey: Apple Academic Press, 2017.
-
Mahapatra DK, Shivhare RS.
Substituting tert-butyl group on Murrayanine-Chalcone Scaffold
Produced Tremendously High Anti-oxidant Activity than the Individual
Components. Int J Anal Med Chem 2018; 1(1): 1-5.
-
Shivhare RS, Mahapatra DK, Nair
RR, Deshmukh SN. Schiff’s base derivatives of murrayanine
demonstrated enhanced anti-oxidant activity than its parent moiety.
Indian J Pharm Edu Res 2016; 50(4): 9-15.
-
Mahapatra DK, Shivhare RS.
Synthesizing an anti-oxidant principle
2-(((1-methoxy-9H-carbazol-3-yl)methylene)amino)isoindoline-1,3-dione
from N-aminophthalimide and murrayanine. Inventi Med Chem 2017;
2017(4): 1-3.
-
Mahapatra DK, Dadure KM,
Shivhare RS. Exploring the Site-Specific Influence of Hydroxyl group
in Ring-B of Murrayanine-Chalcone on Edema Reducing Potential. MOJ
Drug Design Devel Ther 2018; 2(4): 191-194.
-
Mahapatra DK, Shivhare RS.
3′,4′-Methylenedioxy Moiety Containing Murrayanine Based
Chalcone as Emerging Anti-inflammatory Agent. J Mod Chem Chem
Technol 2018; 9(1): 12-16.
-
Bashir M, Bano A, Ijaz AS,
Chaudhary BA. Recent developments and biological activities of
N-substituted carbazole derivatives: A review. Molecules 2015;
20(8): 13496-517.
-
Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK, Asati
V. Anti-cancer Chalcones: Structural and molecular targets
perspectives. Eur J Med Chem 2015; 98: 69-114.
-
Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK, Asati
V. Chalcone derivatives: Anti-inflammatory potential and molecular
targets perspectives. Curr Top Med Chem 2017; 17(28): 3146-3169.
-
Murakami Y, Kawata A, Katayama
T, Fujisawa S. Anti-inflammatory Activity of the Artificial
Antioxidants 2-Tert-butyl-4-methoxyphenol (BHA), 2,
6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT) and 2, 4,
6-Tri-tert-butylphenol (TBP), and their Various Combinations. In
Vivo 2015; 29(2): 197-206.
-
Kanhed AA, Mehere AP, Pandey KR,
Mahapatra DK. 4-(2-chloroacetamido) Benzoic Acid Derivatives as
Local Anesthetic Agents: Design, Synthesis, and Characterization. UK
J Pharm Biosci 2016; 4(6): 35-44.
-
Mahapatra DK, Shivhare RS, Kumar
P. Murrayanine-chalcone transformed into novel pyrimidine compounds
demonstrated promising anti-inflammatory activity. Asian J Pharm Res
2018; 8(1): 6-10.